gensbi.recipes.joint_pipeline#
Pipeline for training and using a Joint model for simulation-based inference.
Classes#
Diffusion pipeline for training and using a Joint model for simulation-based inference. |
|
Flow pipeline for training and using a Joint model for simulation-based inference. |
Functions#
|
|
|
Sample structured conditional masks for the Joint model. |
Module Contents#
- class gensbi.recipes.joint_pipeline.JointDiffusionPipeline(model, train_dataset, val_dataset, dim_obs, dim_cond, ch_obs=1, params=None, training_config=None, condition_mask_kind='structured')[source]#
Bases:
gensbi.recipes.pipeline.AbstractPipelineDiffusion pipeline for training and using a Joint model for simulation-based inference.
- Parameters:
train_dataset (grain dataset or iterator over batches) – Training dataset.
val_dataset (grain dataset or iterator over batches) – Validation dataset.
dim_obs (int) – Dimension of the parameter space.
dim_cond (int) – Dimension of the observation space.
ch_obs (int, optional) – Number of channels for the observation space. Default is 1.
params (optional) – Parameters for the Joint model. If None, default parameters are used.
training_config (dict, optional) – Configuration for training. If None, default configuration is used.
condition_mask_kind (str, optional) – Kind of condition mask to use. One of [“structured”, “posterior”].
Examples
Minimal example on how to instantiate and use the JointDiffusionPipeline:
1# %% Imports 2import os 3 4# Set JAX backend (use 'cuda' for GPU, 'cpu' otherwise) 5# os.environ["JAX_PLATFORMS"] = "cuda" 6 7import grain 8import numpy as np 9import jax 10from jax import numpy as jnp 11from gensbi.recipes import JointDiffusionPipeline 12from gensbi.utils.plotting import plot_marginals 13 14from gensbi.models import Simformer, SimformerParams 15import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 16 17from numpyro import distributions as dist 18 19 20from flax import nnx 21 22# %% 23 24theta_prior = dist.Uniform( 25 low=jnp.array([-2.0, -2.0, -2.0]), high=jnp.array([2.0, 2.0, 2.0]) 26) 27 28dim_obs = 3 29dim_cond = 3 30dim_joint = dim_obs + dim_cond 31 32 33# %% 34def simulator(key, nsamples): 35 theta_key, sample_key = jax.random.split(key, 2) 36 thetas = theta_prior.sample(theta_key, (nsamples,)) 37 38 xs = thetas + 1 + jax.random.normal(sample_key, thetas.shape) * 0.1 39 40 thetas = thetas[..., None] 41 xs = xs[..., None] 42 43 # when making a dataset for the joint pipeline, thetas need to come first 44 data = jnp.concatenate([thetas, xs], axis=1) 45 46 return data 47 48 49# %% Define your training and validation datasets. 50# We generate a training dataset and a validation dataset using the simulator. 51# The simulator is a simple function that generates parameters (theta) and data (x). 52# In this example, we use a simple Gaussian simulator. 53train_data = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(0), 100_000) 54val_data = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(1), 2000) 55# %% Normalize the dataset 56# It is important to normalize the data to have zero mean and unit variance. 57# This helps the model training process. 58means = jnp.mean(train_data, axis=0) 59stds = jnp.std(train_data, axis=0) 60 61 62def normalize(data, means, stds): 63 return (data - means) / stds 64 65 66def unnormalize(data, means, stds): 67 return data * stds + means 68 69 70# %% Prepare the data for the pipeline 71# The pipeline expects the data to be normalized but not split (for joint pipelines). 72 73 74def process_data(data): 75 return normalize(data, means, stds) 76 77 78# %% 79train_data.shape 80 81# %% 82 83# %% Create the input pipeline using Grain 84# We use Grain to create an efficient input pipeline. 85# This involves shuffling, repeating for multiple epochs, and batching the data. 86# We also map the process_data function to prepare (normalize) the data for the model. 87batch_size = 256 88 89train_dataset_grain = ( 90 grain.MapDataset.source(np.array(train_data)) 91 .shuffle(42) 92 .repeat() 93 .to_iter_dataset() 94 .batch(batch_size) 95 .map(process_data) 96 # .mp_prefetch() # Uncomment if you want to use multiprocessing prefetching 97) 98 99val_dataset_grain = ( 100 grain.MapDataset.source(np.array(val_data)) 101 .shuffle( 102 42 103 ) # Use a different seed/strategy for validation if needed, but shuffling is fine 104 .repeat() 105 .to_iter_dataset() 106 .batch(batch_size) 107 .map(process_data) 108 # .mp_prefetch() # Uncomment if you want to use multiprocessing prefetching 109) 110 111# %% Define your model 112# specific model parameters are defined here. 113# For Simformer, we need to specify dimensions, embedding strategies, and other architecture details. 114params = SimformerParams( 115 rngs=nnx.Rngs(0), 116 in_channels=1, 117 dim_value=20, 118 dim_id=10, 119 dim_condition=10, 120 dim_joint=dim_joint, 121 fourier_features=128, 122 num_heads=4, 123 num_layers=6, 124 widening_factor=3, 125 qkv_features=40, 126 num_hidden_layers=1, 127) 128 129model = Simformer(params) 130 131# %% Instantiate the pipeline 132# The JointDiffusionPipeline handles the training loop and sampling. 133# We configure it with the model, datasets, dimensions using a default training configuration. 134# We also specify the condition_mask_kind, which determines how conditioning is handled during training. 135training_config = JointDiffusionPipeline.get_default_training_config() 136training_config["nsteps"] = 10000 137 138pipeline = JointDiffusionPipeline( 139 model, 140 train_dataset_grain, 141 val_dataset_grain, 142 dim_obs, 143 dim_cond, 144 condition_mask_kind="posterior", 145 training_config=training_config, 146) 147 148# %% Train the model 149# We create a random key for training and start the training process. 150rngs = nnx.Rngs(42) 151pipeline.train( 152 rngs, save_model=False 153) # if you want to save the model, set save_model=True 154 155# %% Sample from the posterior 156# To generate samples, we first need an observation (and its corresponding condition). 157# We generate a new sample from the simulator, normalize it, and extract the condition x_o. 158 159new_sample = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(20), 1) 160true_theta = new_sample[:, :dim_obs, :] # extract observation from the joint sample 161 162new_sample = normalize(new_sample, means, stds) 163x_o = new_sample[:, dim_obs:, :] # extract condition from the joint sample 164 165# Then we invoke the pipeline's sample method. 166samples = pipeline.sample(rngs.sample(), x_o, nsamples=100_000) 167# Finally, we unnormalize the samples to get them back to the original scale. 168samples = unnormalize(samples, means[:dim_obs], stds[:dim_obs]) 169 170# %% Plot the samples 171# We verify the model's performance by plotting the marginal distributions of the generated samples 172# against the true parameters. 173plot_marginals( 174 np.array(samples[..., 0]), 175 gridsize=30, 176 true_param=np.array(true_theta[0, :, 0]), 177 range=[(1, 3), (1, 3), (-0.6, 0.5)], 178) 179plt.savefig("joint_diffusion_pipeline_marginals.png", dpi=100, bbox_inches="tight") 180plt.show()
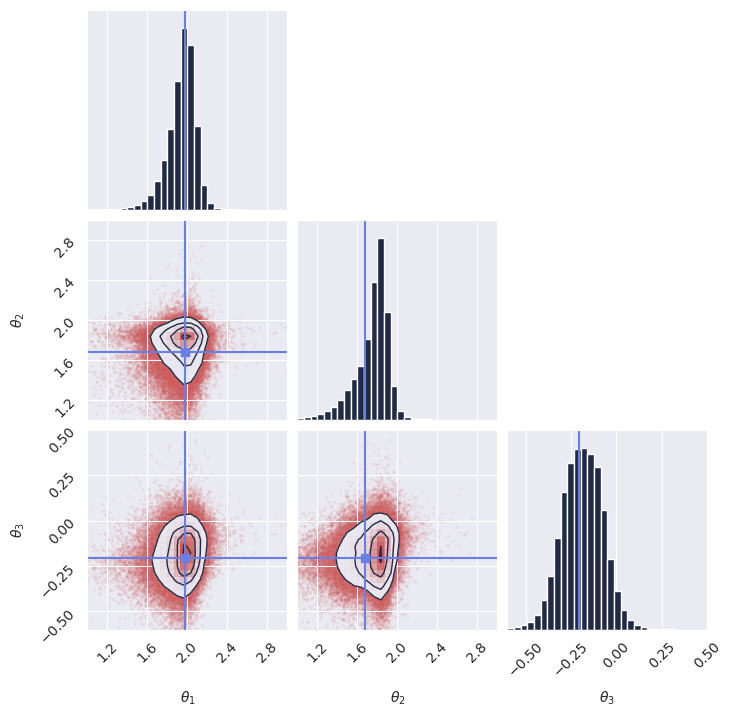
Note
If you plan on using multiprocessing prefetching, ensure that your script is wrapped in a
if __name__ == "__main__":guard. See https://docs.python.org/3/library/multiprocessing.html- _wrap_model()[source]#
Wrap the model for evaluation (either using JointWrapper or ConditionalWrapper).
- classmethod get_default_training_config()[source]#
Return a dictionary of default training configuration parameters.
- Returns:
training_config – Default training configuration.
- Return type:
dict
- get_sampler(x_o, nsteps=18, use_ema=True, return_intermediates=False, **model_extras)[source]#
Get a sampler function for generating samples from the trained model.
- Parameters:
key (jax.random.PRNGKey) – Random number generator key.
x_o (array-like) – Conditioning variable.
step_size (float, optional) – Step size for the sampler.
use_ema (bool, optional) – Whether to use the EMA model for sampling.
time_grid (array-like, optional) – Time grid for the sampler (if applicable).
model_extras (dict, optional) – Additional model-specific parameters.
- Returns:
sampler – A function that generates samples when called with a random key and number of samples.
- Return type:
Callable: key, nsamples -> samples
- classmethod init_pipeline_from_config()[source]#
- Abstractmethod:
Initialize the pipeline from a configuration file.
- Parameters:
train_dataset (iterable) – Training dataset.
val_dataset (iterable) – Validation dataset.
dim_obs (int) – Dimensionality of the parameter (theta) space.
dim_cond (int) – Dimensionality of the observation (x) space.
config_path (str) – Path to the configuration file.
checkpoint_dir (str) – Directory for saving checkpoints.
- Returns:
pipeline – An instance of the pipeline initialized from the configuration.
- Return type:
- sample(key, x_o, nsamples=10000, nsteps=18, use_ema=True, return_intermediates=False, **model_extras)[source]#
Generate samples from the trained model.
- Parameters:
key (jax.random.PRNGKey) – Random number generator key.
x_o (array-like) – Conditioning variable (e.g., observed data).
nsamples (int, optional) – Number of samples to generate.
- Returns:
samples – Generated samples of size (nsamples, dim_obs, ch_obs).
- Return type:
array-like
- class gensbi.recipes.joint_pipeline.JointFlowPipeline(model, train_dataset, val_dataset, dim_obs, dim_cond, ch_obs=1, params=None, training_config=None, condition_mask_kind='structured')[source]#
Bases:
gensbi.recipes.pipeline.AbstractPipelineFlow pipeline for training and using a Joint model for simulation-based inference.
- Parameters:
train_dataset (grain dataset or iterator over batches) – Training dataset.
val_dataset (grain dataset or iterator over batches) – Validation dataset.
dim_obs (int) – Dimension of the parameter space.
dim_cond (int) – Dimension of the observation space.
ch_obs (int, optional) – Number of channels for the observation space. Default is 1.
params (JointParams, optional) – Parameters for the Joint model. If None, default parameters are used.
training_config (dict, optional) – Configuration for training. If None, default configuration is used.
condition_mask_kind (str, optional) – Kind of condition mask to use. One of [“structured”, “posterior”].
Examples
Minimal example on how to instantiate and use the JointFlowPipeline:
1# %% Imports 2import os 3 4# Set JAX backend (use 'cuda' for GPU, 'cpu' otherwise) 5# os.environ["JAX_PLATFORMS"] = "cuda" 6 7import grain 8import numpy as np 9import jax 10from jax import numpy as jnp 11from numpyro import distributions as dist 12from flax import nnx 13 14from gensbi.recipes import JointFlowPipeline 15from gensbi.models import Simformer, SimformerParams 16 17from gensbi.utils.plotting import plot_marginals 18import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 19 20 21# %% 22 23theta_prior = dist.Uniform( 24 low=jnp.array([-2.0, -2.0, -2.0]), high=jnp.array([2.0, 2.0, 2.0]) 25) 26 27dim_obs = 3 28dim_cond = 3 29dim_joint = dim_obs + dim_cond 30 31 32# %% 33def simulator(key, nsamples): 34 theta_key, sample_key = jax.random.split(key, 2) 35 thetas = theta_prior.sample(theta_key, (nsamples,)) 36 37 xs = thetas + 1 + jax.random.normal(sample_key, thetas.shape) * 0.1 38 39 thetas = thetas[..., None] 40 xs = xs[..., None] 41 42 # when making a dataset for the joint pipeline, thetas need to come first 43 data = jnp.concatenate([thetas, xs], axis=1) 44 45 return data 46 47 48# %% Define your training and validation datasets. 49# We generate a training dataset and a validation dataset using the simulator. 50# The simulator is a simple function that generates parameters (theta) and data (x). 51# In this example, we use a simple Gaussian simulator. 52train_data = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(0), 100_000) 53val_data = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(1), 2000) 54# %% Normalize the dataset 55# It is important to normalize the data to have zero mean and unit variance. 56# This helps the model training process. 57means = jnp.mean(train_data, axis=0) 58stds = jnp.std(train_data, axis=0) 59 60 61def normalize(data, means, stds): 62 return (data - means) / stds 63 64 65def unnormalize(data, means, stds): 66 return data * stds + means 67 68 69# %% Prepare the data for the pipeline 70# The pipeline expects the data to be normalized but not split (for joint pipelines). 71 72 73# %% Prepare the data for the pipeline 74# The pipeline expects the data to be normalized but not split (for joint pipelines). 75def process_data(data): 76 return normalize(data, means, stds) 77 78 79# %% 80train_data.shape 81 82# %% 83 84# %% Create the input pipeline using Grain 85# We use Grain to create an efficient input pipeline. 86# This involves shuffling, repeating for multiple epochs, and batching the data. 87# We also map the process_data function to prepare (normalize) the data for the model. 88# We also map the process_data function to prepare (normalize) the data for the model. 89# %% Create the input pipeline using Grain 90# We use Grain to create an efficient input pipeline. 91# This involves shuffling, repeating for multiple epochs, and batching the data. 92# We also map the process_data function to prepare (normalize) the data for the model. 93batch_size = 256 94 95train_dataset_grain = ( 96 grain.MapDataset.source(np.array(train_data)) 97 .shuffle(42) 98 .repeat() 99 .to_iter_dataset() 100 .batch(batch_size) 101 .map(process_data) 102 # .mp_prefetch() # Uncomment if you want to use multiprocessing prefetching 103) 104 105val_dataset_grain = ( 106 grain.MapDataset.source(np.array(val_data)) 107 .shuffle(42) 108 .repeat() 109 .to_iter_dataset() 110 .batch(batch_size) 111 .map(process_data) 112 # .mp_prefetch() # Uncomment if you want to use multiprocessing prefetching 113) 114 115# %% Define your model 116# specific model parameters are defined here. 117# For Simformer, we need to specify dimensions, embedding strategies, and other architecture details. 118params = SimformerParams( 119 rngs=nnx.Rngs(0), 120 in_channels=1, 121 dim_value=20, 122 dim_id=10, 123 dim_condition=10, 124 dim_joint=dim_joint, 125 fourier_features=128, 126 num_heads=4, 127 num_layers=6, 128 widening_factor=3, 129 qkv_features=40, 130 num_hidden_layers=1, 131) 132 133model = Simformer(params) 134 135# %% Instantiate the pipeline 136# The JointFlowPipeline handles the training loop and sampling. 137# We configure it with the model, datasets, dimensions using a default training configuration. 138# We also specify the condition_mask_kind, which determines how conditioning is handled during training. 139training_config = JointFlowPipeline.get_default_training_config() 140training_config["nsteps"] = 10000 141 142pipeline = JointFlowPipeline( 143 model, 144 train_dataset_grain, 145 val_dataset_grain, 146 dim_obs, 147 dim_cond, 148 condition_mask_kind="posterior", 149 training_config=training_config, 150) 151 152# %% Train the model 153# We create a random key for training and start the training process. 154rngs = nnx.Rngs(42) 155pipeline.train( 156 rngs, save_model=False 157) # if you want to save the model, set save_model=True 158 159# %% Sample from the posterior 160# To generate samples, we first need an observation (and its corresponding condition). 161# We generate a new sample from the simulator, normalize it, and extract the condition x_o. 162 163new_sample = simulator(jax.random.PRNGKey(20), 1) 164true_theta = new_sample[:, :dim_obs, :] # extract observation from the joint sample 165 166new_sample = normalize(new_sample, means, stds) 167x_o = new_sample[:, dim_obs:, :] # extract condition from the joint sample 168 169# Then we invoke the pipeline's sample method. 170samples = pipeline.sample(rngs.sample(), x_o, nsamples=100_000) 171# Finally, we unnormalize the samples to get them back to the original scale. 172samples = unnormalize(samples, means[:dim_obs], stds[:dim_obs]) 173 174# %% Plot the samples 175# We verify the model's performance by plotting the marginal distributions of the generated samples 176# against the true parameters. 177plot_marginals( 178 np.array(samples[..., 0]), 179 gridsize=30, 180 true_param=np.array(true_theta[0, :, 0]), 181 range=[(1, 3), (1, 3), (-0.6, 0.5)], 182) 183plt.savefig("joint_flow_pipeline_marginals.png", dpi=100, bbox_inches="tight") 184plt.show()
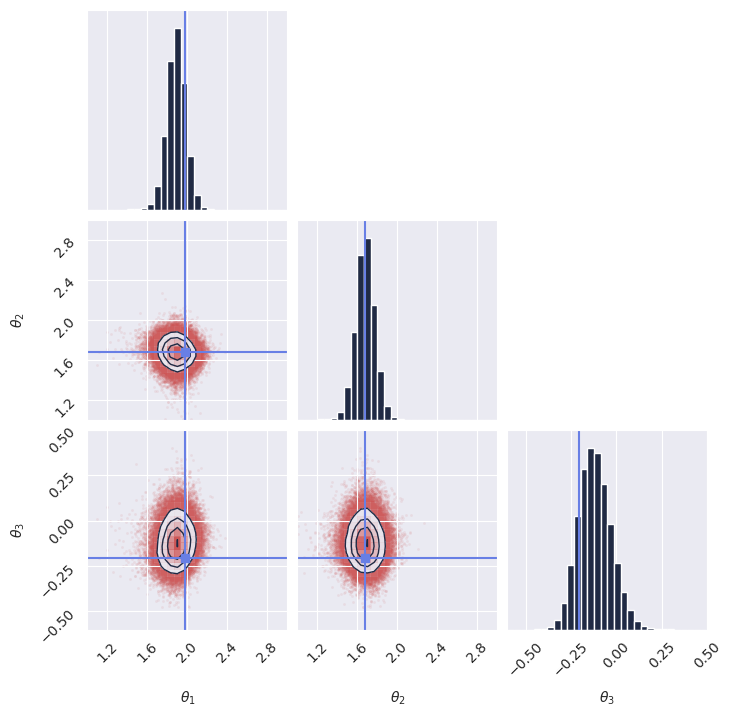
Note
If you plan on using multiprocessing prefetching, ensure that your script is wrapped in a
if __name__ == "__main__":guard. See https://docs.python.org/3/library/multiprocessing.html- _wrap_model()[source]#
Wrap the model for evaluation (either using JointWrapper or ConditionalWrapper).
- get_sampler(x_o, step_size=0.01, use_ema=True, time_grid=None, **model_extras)[source]#
Get a sampler function for generating samples from the trained model.
- Parameters:
key (jax.random.PRNGKey) – Random number generator key.
x_o (array-like) – Conditioning variable.
step_size (float, optional) – Step size for the sampler.
use_ema (bool, optional) – Whether to use the EMA model for sampling.
time_grid (array-like, optional) – Time grid for the sampler (if applicable).
model_extras (dict, optional) – Additional model-specific parameters.
- Returns:
sampler – A function that generates samples when called with a random key and number of samples.
- Return type:
Callable: key, nsamples -> samples
- classmethod init_pipeline_from_config()[source]#
- Abstractmethod:
Initialize the pipeline from a configuration file.
- Parameters:
train_dataset (iterable) – Training dataset.
val_dataset (iterable) – Validation dataset.
dim_obs (int) – Dimensionality of the parameter (theta) space.
dim_cond (int) – Dimensionality of the observation (x) space.
config_path (str) – Path to the configuration file.
checkpoint_dir (str) – Directory for saving checkpoints.
- Returns:
pipeline – An instance of the pipeline initialized from the configuration.
- Return type:
- sample(key, x_o, nsamples=10000, step_size=0.01, use_ema=True, time_grid=None, **model_extras)[source]#
Generate samples from the trained model.
- Parameters:
key (jax.random.PRNGKey) – Random number generator key.
x_o (array-like) – Conditioning variable (e.g., observed data).
nsamples (int, optional) – Number of samples to generate.
- Returns:
samples – Generated samples of size (nsamples, dim_obs, ch_obs).
- Return type:
array-like
- gensbi.recipes.joint_pipeline.sample_condition_mask(key, num_samples, theta_dim, x_dim, kind='structured')[source]#
- gensbi.recipes.joint_pipeline.sample_structured_conditional_mask(key, num_samples, theta_dim, x_dim, p_joint=0.2, p_posterior=0.2, p_likelihood=0.2, p_rnd1=0.2, p_rnd2=0.2, rnd1_prob=0.3, rnd2_prob=0.7)[source]#
Sample structured conditional masks for the Joint model.
- Parameters:
key (jax.random.PRNGKey) – Random key for sampling.
num_samples (int) – Number of samples to generate.
theta_dim (int) – Dimension of the parameter space.
x_dim (int) – Dimension of the observation space.
p_joint (float) – Probability of selecting the joint mask.
p_posterior (float) – Probability of selecting the posterior mask.
p_likelihood (float) – Probability of selecting the likelihood mask.
p_rnd1 (float) – Probability of selecting the first random mask.
p_rnd2 (float) – Probability of selecting the second random mask.
rnd1_prob (float) – Probability of a True value in the first random mask.
rnd2_prob (float) – Probability of a True value in the second random mask.
- Returns:
condition_mask – Array of shape (num_samples, theta_dim + x_dim) with boolean masks.
- Return type:
jnp.ndarray
